Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic Eye Disease Treatment in Houston, TX
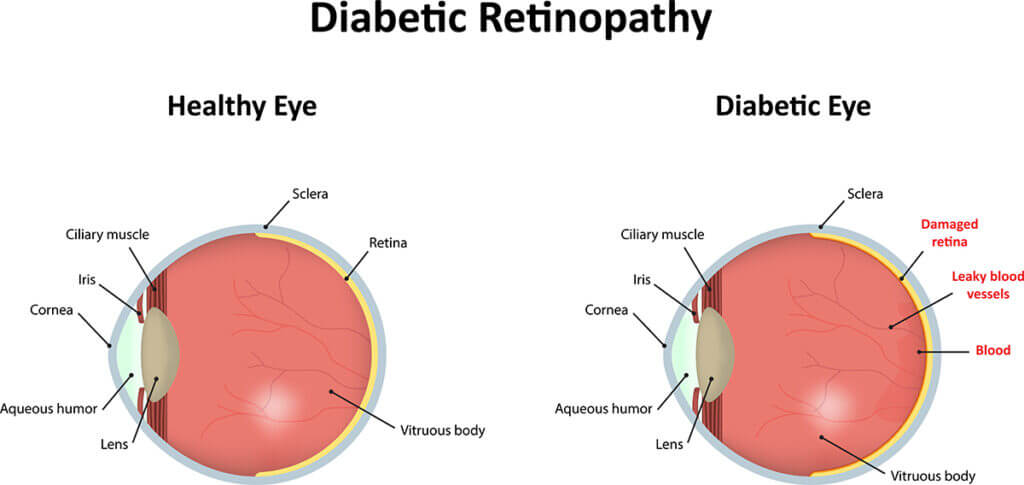
Diabetes is a disease that affects the body’s ability to produce or use insulin effectively to control blood sugar (glucose) levels. Too much glucose in the blood for a long time can cause damage in many parts of the body. Diabetes can damage the heart, kidneys and blood vessels. It damages small blood vessels in the eye as well.
Download Diabetic Retinopathy Information
What Is Diabetic Eye Disease?
Diabetic eye disease is a term for several eye problems that can all result from diabetes. Diabetic eye disease includes: